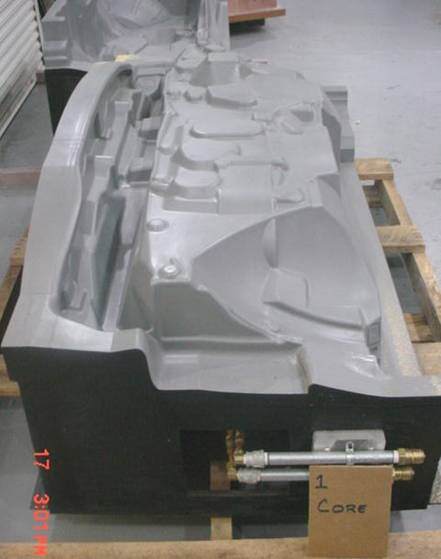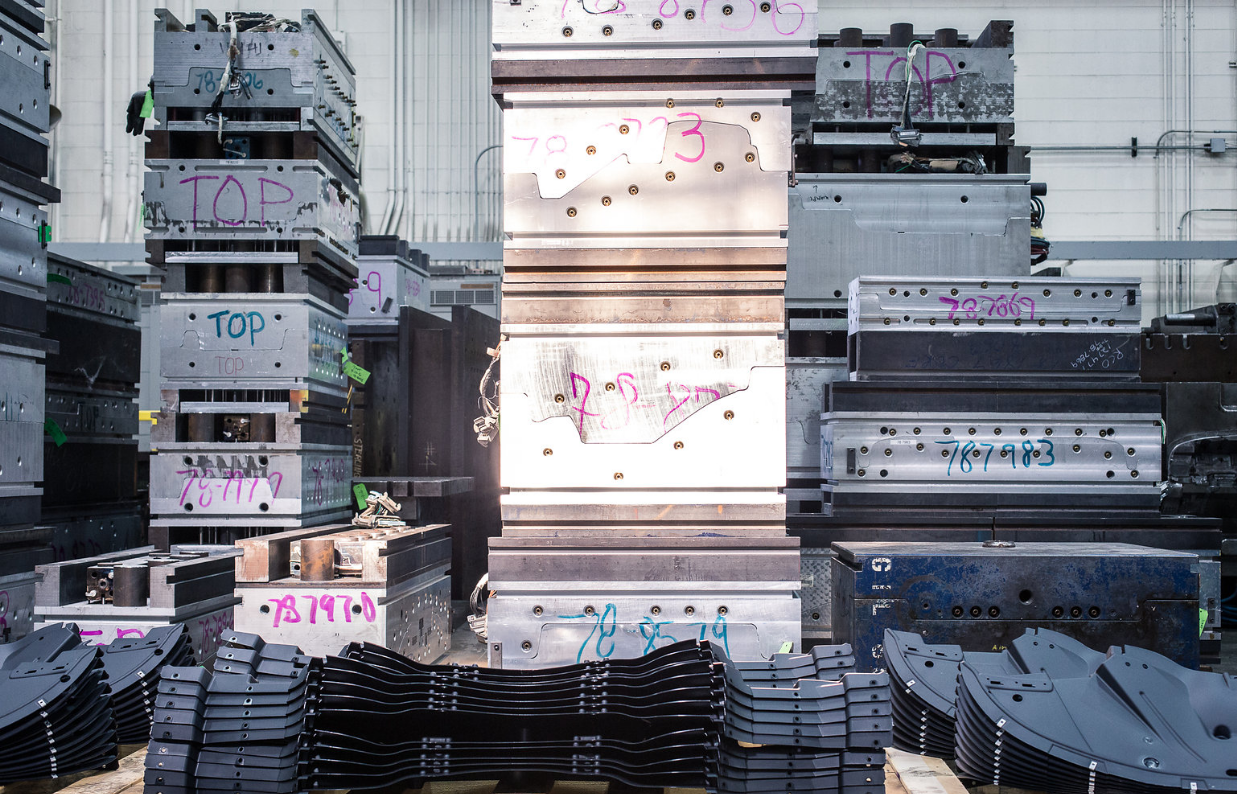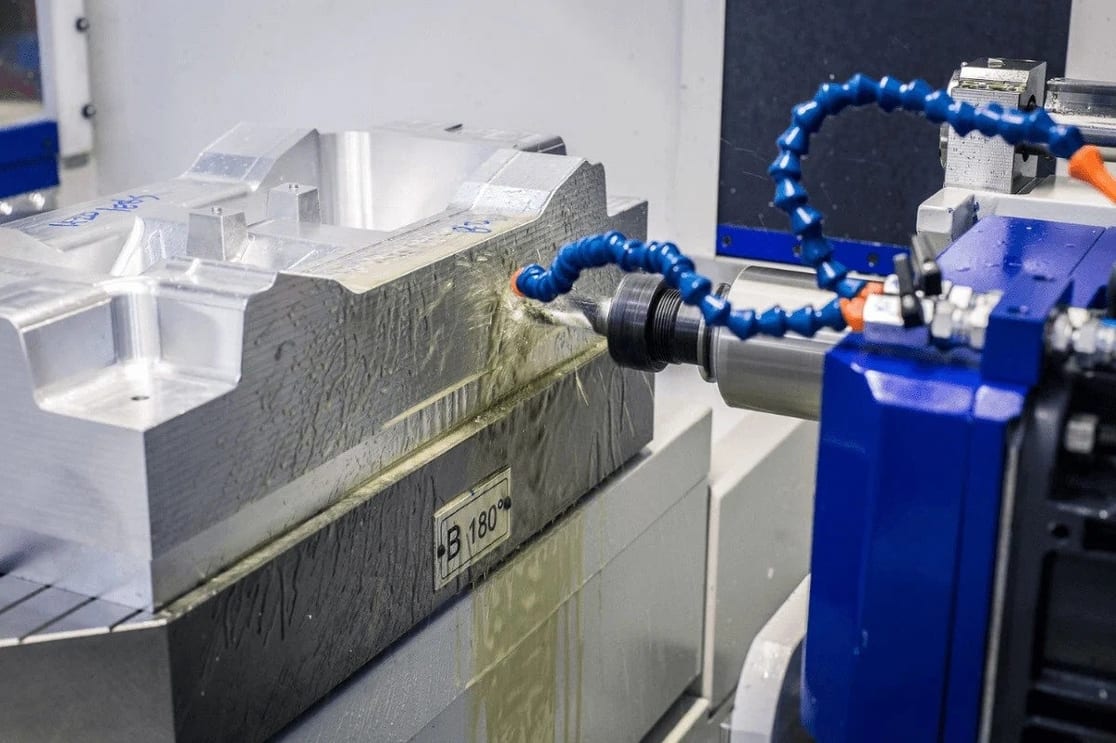
Since RCO's inception we've built injection molds, cast aluminum tooling, stamping dies, and custom prototype tools for the automotive, defense, and aerospace industries. RCO relies on its dedicated tool design & engineering team, machining centers, and pattern shop to complete every tooling job in-house and on time. Our diversity of experience and vertically integrated campus gives us the ability to meet very tight timing while maintaining the quality you expect.

Tool materials
- PINE
- SAND
- RENBOARD
- HIGH TEMP EPOXY
- CAST ALUMINUM
- BILLET ALUMINUM
- MILD STEEL
- P20 STEEL
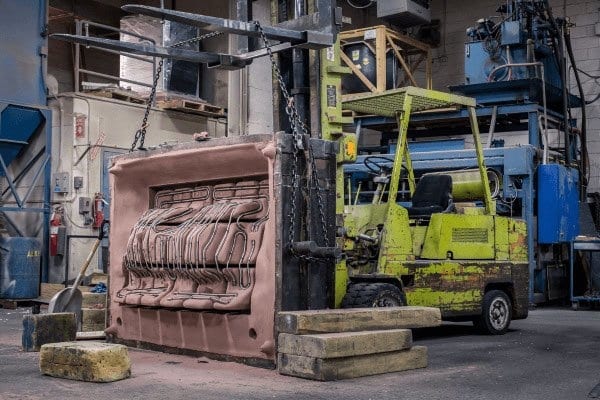

We Make Tools for
- COMPRESSION MOLD
- INJECTION MOLD
- MOLDED FOAM
- VACUUM FORMING
- THERMOFORMING
- METAL STAMPING

Commodities We Support
- PLASTIC
- COMPOSITES
- POLYURETHANE FOAM
- ACOUSTICAL
- SHEET METAL AND ALUMINUM
- SOFT TRIM



What Is Prototype Tooling?
Prototype tooling is a type of mold used to produce a small number of parts for evaluation or testing purposes. Prototype molds are typically made from aluminum or steel and can be used to produce prototype parts in both plastic and metal.
The main advantage of using prototype tooling is that it allows you to quickly and inexpensively test out your design ideas before committing to the cost and time of manufacturing a full production mold.
Prototype tooling is one of the most crucial aspects of any manufacturing process. Without prototype tooling or injection mold tooling, production cannot take place.
What Is Tool Building?
Tool building is the process of creating the prototype tooling or injection mold tooling necessary for production. This can be done in-house or contracted out to a third party.
Some prototype tooling is made by hand with little to no automation, while others use advanced technology and automated machines to create the prototype tools needed for production parts.
The benefit of tool building is that you can produce a prototype of the part you need without having to go into full-scale production. This allows for faster iteration times and reduced costs.
Types of Prototype Tooling
There are three main types of prototype tooling:
Injection molds: Used to produce plastic parts
Compression molds: Used to produce metal or plastic parts
Stampings dies: Used to create metal parts through stamping
Compression molds: Used to produce metal or plastic parts
Stampings dies: Used to create metal parts through stamping
In each type of prototype tooling, there are a variety of specialized molds and dies that can be used depending on the part you are trying to produce.

.png)

How is prototype tooling or (soft tooling) used in the automotive industry
Prototype tooling, also known as soft tooling, plays a critical role in the automotive industry by enabling the production of low-cost, low-volume parts for testing, validation, and early development stages. Here's how it's used:
1. Rapid Prototyping for Design Validation
Prototype tooling is commonly used to create parts quickly for design validation. Engineers and designers can test how components fit and function within a vehicle’s overall design before committing to more expensive hard tooling for mass production.
2. Functional Testing
Automotive parts made with prototype tooling are often used for functional testing. This allows manufacturers to assess the performance, durability, and reliability of components under real-world conditions, ensuring they meet quality and safety standards.
3. Cost-Effective Customization
Soft tooling is ideal for producing small batches of customized or experimental parts, especially for concept cars, specialty vehicles, or limited-edition models. It allows manufacturers to iterate designs without the high upfront costs associated with hard tooling.
4. Accelerated Time-to-Market
In the fast-paced automotive industry, reducing development time is essential. Soft tooling enables rapid production of parts, helping automakers bring new models to market faster while still refining and improving designs.
5. Bridge Tooling Between Prototyping and Mass Production
Prototype tooling serves as a bridge for low-volume production while the final hard tooling is being prepared. This ensures manufacturers can begin limited production or pilot runs without delays.
For more insights into how prototype tooling is shaping innovation in the automotive sector, explore this comprehensive guide: Sheet Metal Soft Tooling vs. Hard Tooling to learn how these technologies are driving efficiency and precision in automotive manufacturing.
1. Rapid Prototyping for Design Validation
Prototype tooling is commonly used to create parts quickly for design validation. Engineers and designers can test how components fit and function within a vehicle’s overall design before committing to more expensive hard tooling for mass production.
2. Functional Testing
Automotive parts made with prototype tooling are often used for functional testing. This allows manufacturers to assess the performance, durability, and reliability of components under real-world conditions, ensuring they meet quality and safety standards.
3. Cost-Effective Customization
Soft tooling is ideal for producing small batches of customized or experimental parts, especially for concept cars, specialty vehicles, or limited-edition models. It allows manufacturers to iterate designs without the high upfront costs associated with hard tooling.
4. Accelerated Time-to-Market
In the fast-paced automotive industry, reducing development time is essential. Soft tooling enables rapid production of parts, helping automakers bring new models to market faster while still refining and improving designs.
5. Bridge Tooling Between Prototyping and Mass Production
Prototype tooling serves as a bridge for low-volume production while the final hard tooling is being prepared. This ensures manufacturers can begin limited production or pilot runs without delays.
For more insights into how prototype tooling is shaping innovation in the automotive sector, explore this comprehensive guide: Sheet Metal Soft Tooling vs. Hard Tooling to learn how these technologies are driving efficiency and precision in automotive manufacturing.
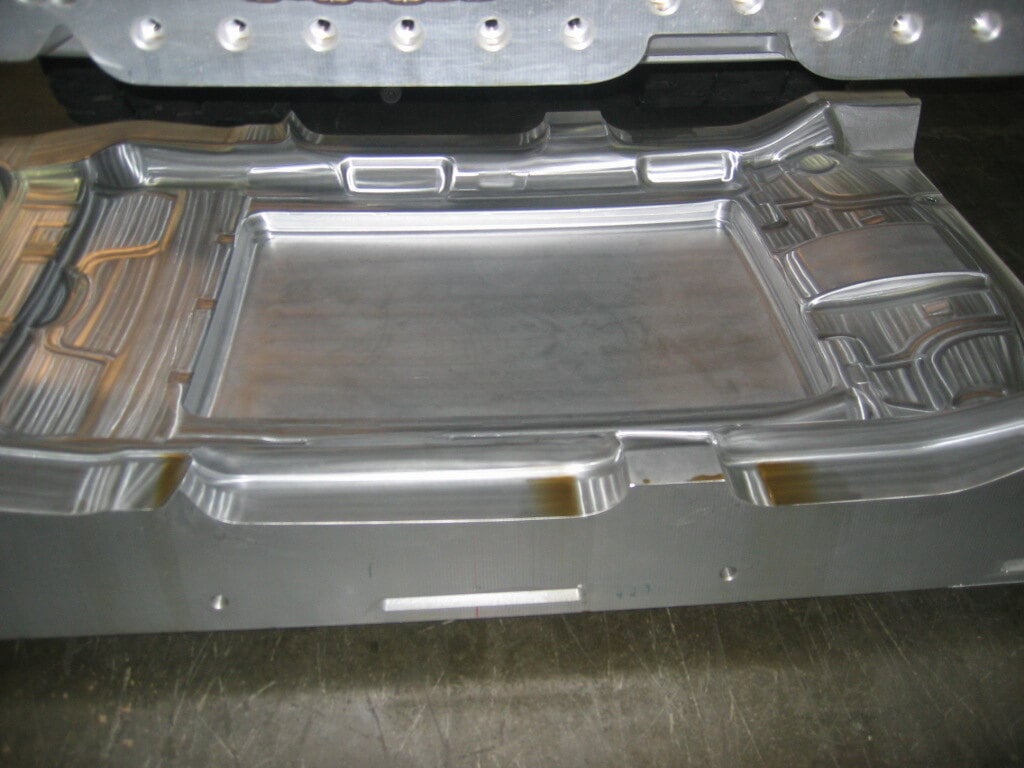
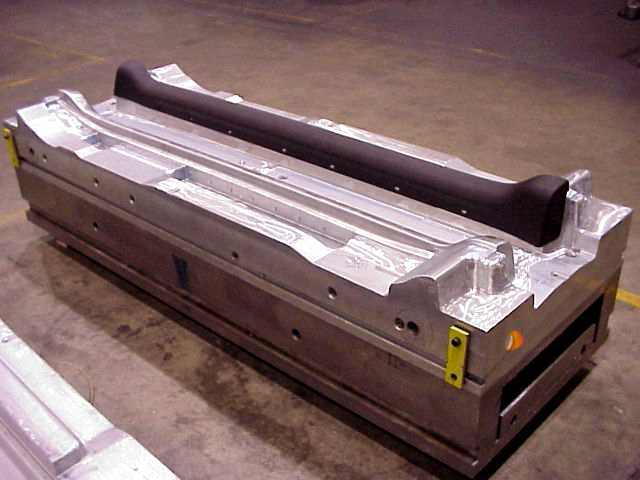
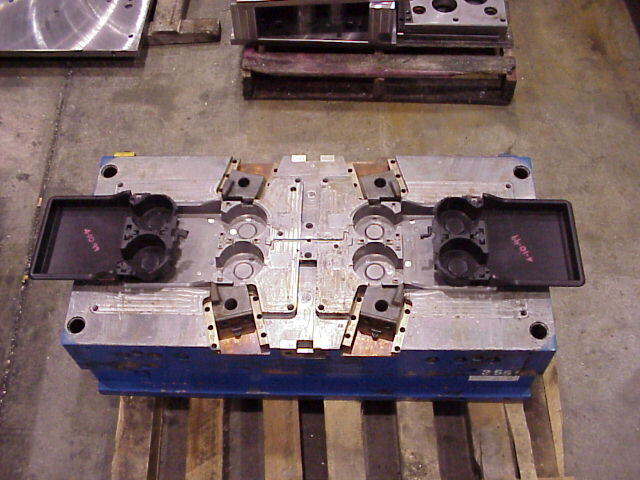


What types of automotive components can be made with prototype tooling?
Soft tooling, or prototype tooling, is highly versatile in the automotive industry and is used to manufacture a variety of components. Here are specific examples of automotive products that can be made with soft tooling:
1. Exterior Body Panels
Soft tooling is used to produce limited runs of exterior parts such as:
Fenders
Hoods
Door panels
These components are often created for prototype vehicles or specialty models.
1. Exterior Body Panels
Soft tooling is used to produce limited runs of exterior parts such as:
Fenders
Hoods
Door panels
These components are often created for prototype vehicles or specialty models.
2. Interior Trim Components
Low-volume runs of interior parts can be made using soft tooling, including:
Dashboard panels
Door trims
Seat shells
These parts are often tested for fit, aesthetics, and ergonomics.
Low-volume runs of interior parts can be made using soft tooling, including:
Dashboard panels
Door trims
Seat shells
These parts are often tested for fit, aesthetics, and ergonomics.
3. Functional Under-the-Hood Parts
Parts like engine covers, brackets, and air ducts are commonly produced with soft tooling for early testing and design refinement.
4. Lighting and Reflector Housings
Prototypes of headlight and taillight housings are made with soft tooling to test illumination, fit, and overall design.
Prototypes of headlight and taillight housings are made with soft tooling to test illumination, fit, and overall design.
5. Custom or Specialty Parts
For concept cars or limited-edition models, soft tooling enables the production of unique, low-volume parts such as:
Custom grille designs
Spoilers
Emblems or badging
For concept cars or limited-edition models, soft tooling enables the production of unique, low-volume parts such as:
Custom grille designs
Spoilers
Emblems or badging
6. Structural Components for Testing
Chassis components, cross members, and mounting brackets are often manufactured with soft tooling for stress and durability testing during vehicle development.
Chassis components, cross members, and mounting brackets are often manufactured with soft tooling for stress and durability testing during vehicle development.
7. Early-stage Molded Parts
Prototypes for plastic parts like air vents, control knobs, and console components can be quickly and cost-effectively created with soft tooling.
By enabling the production of these diverse components, soft tooling allows manufacturers to refine designs, test functionality, and speed up development timelines before moving to mass production.
Prototypes for plastic parts like air vents, control knobs, and console components can be quickly and cost-effectively created with soft tooling.
By enabling the production of these diverse components, soft tooling allows manufacturers to refine designs, test functionality, and speed up development timelines before moving to mass production.




